502 Error Troubleshooting Guide
This guide explains the most common causes of 502 Bad Gateway errors and how to fix them.
1. PHP-FPM Not Running
A 502 Bad Gateway error is common when using Nginx. It means the web server (Nginx) did not receive a response from the backend (such as PHP-FPM, Node.js, or Python).
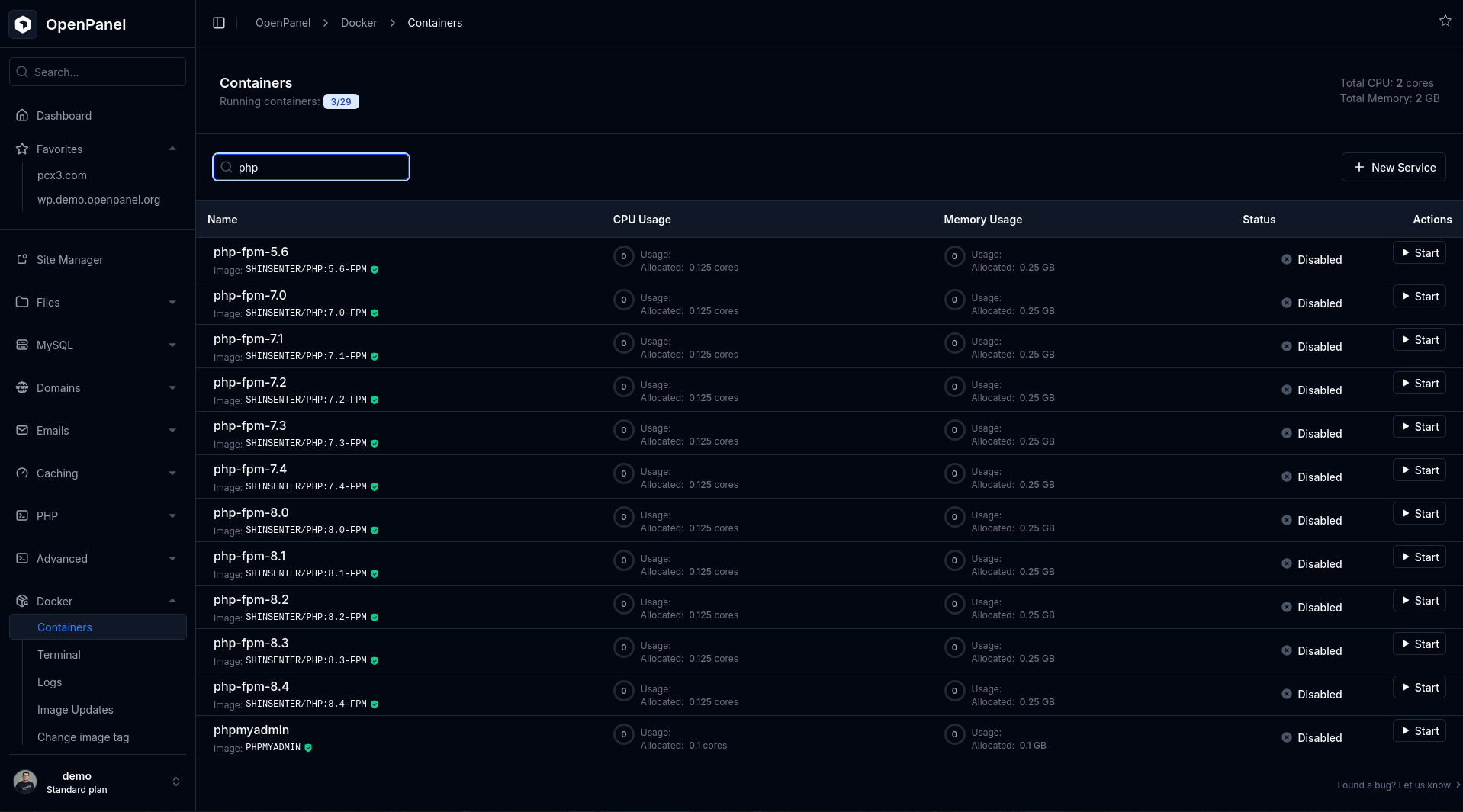
Steps to check PHP-FPM:
- Verify that the PHP service is running.
If Docker feature is enabled, go to Docker > Containers and check the status of the PHP container.
If inactive, start it.
2. Restart Nginx
Even if PHP-FPM is running, Nginx may have started before it and failed to connect on the first attempt, causing cached errors.
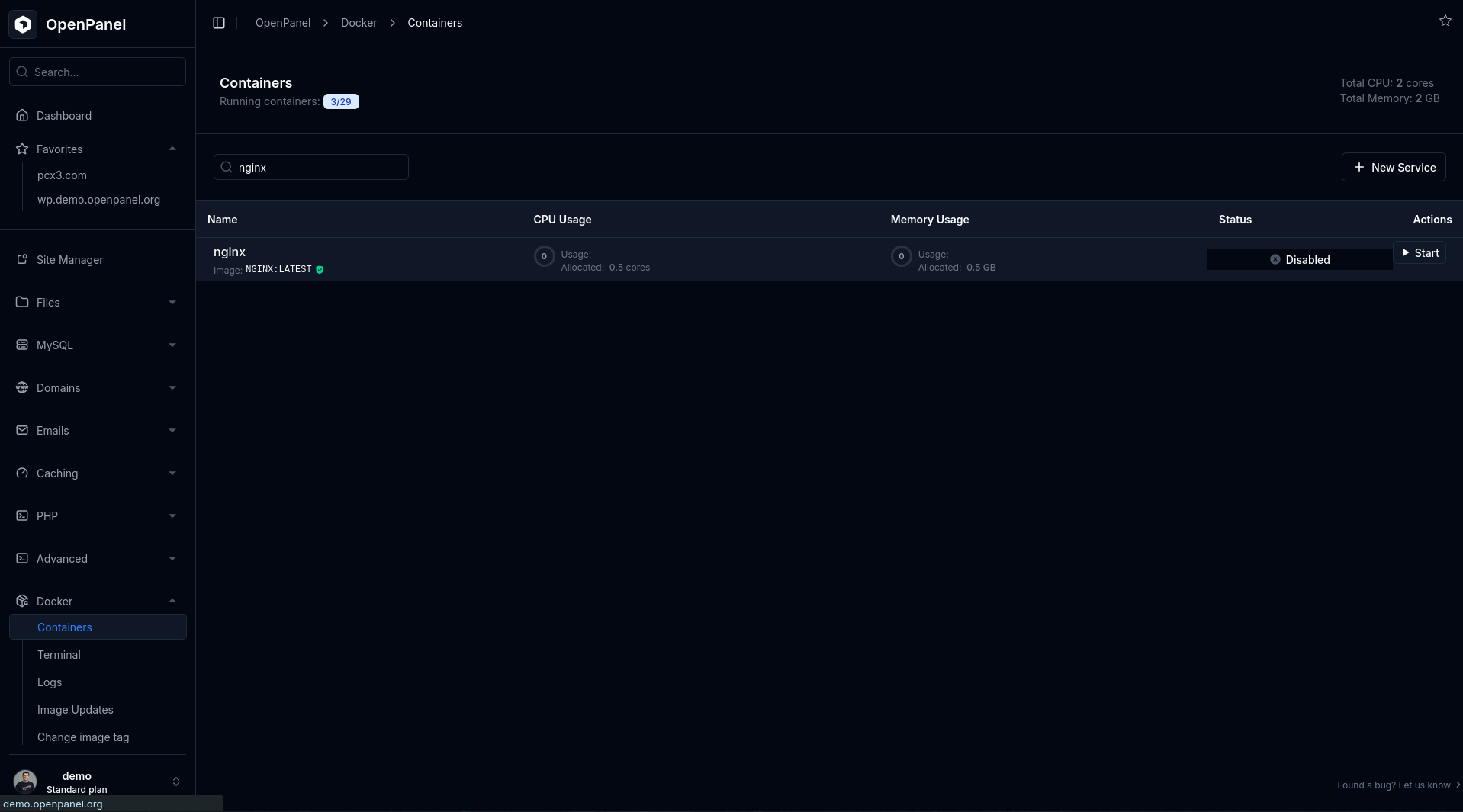
Fix: Restart Nginx.
If using Docker feature: Go to Docker > Containers, disable Nginx, then enable it again.
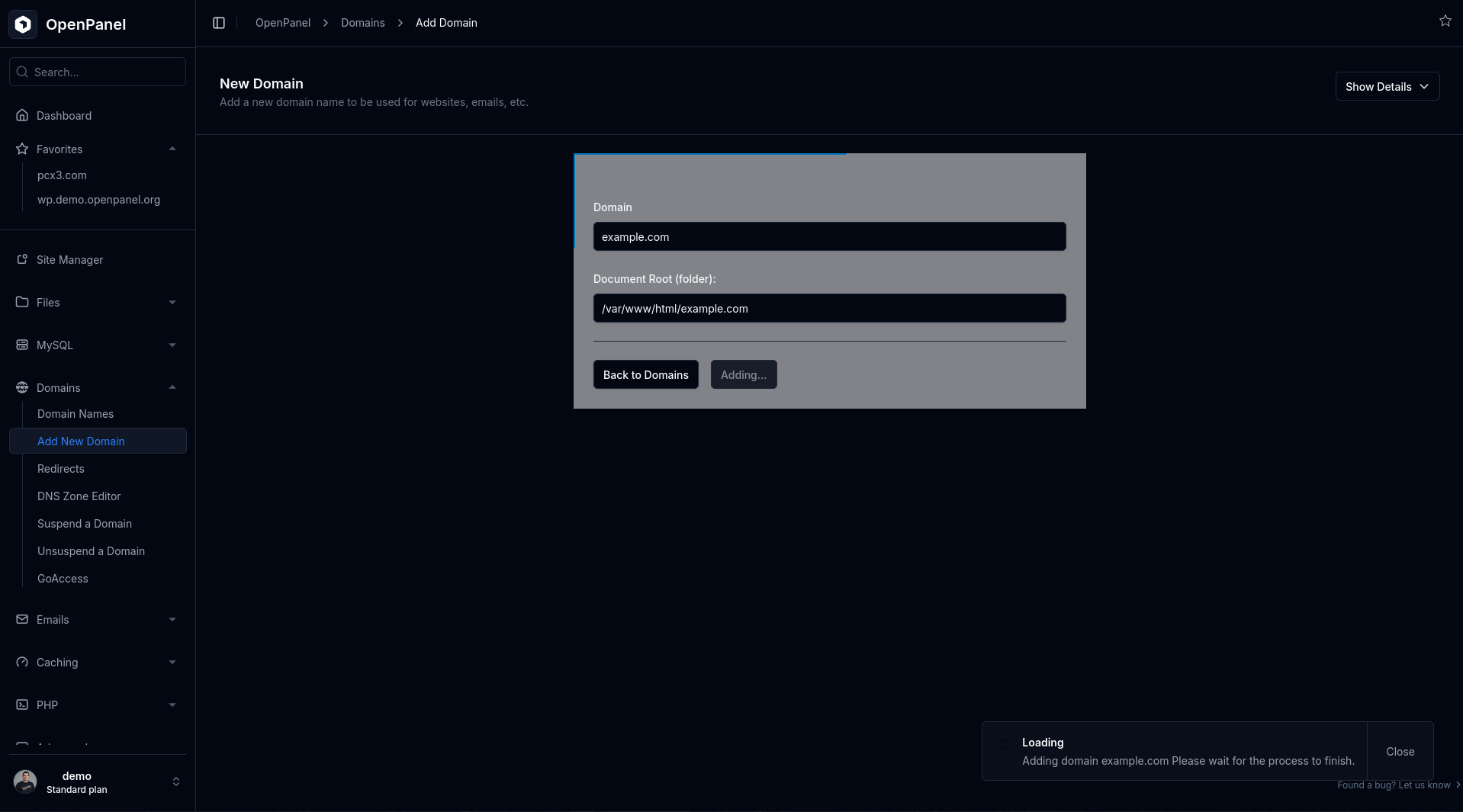
If you do not have access to Docker feature, simply add another domain in order to restart Nginx: Go to Domains > Add New, insert domain name and click on 'Add'.
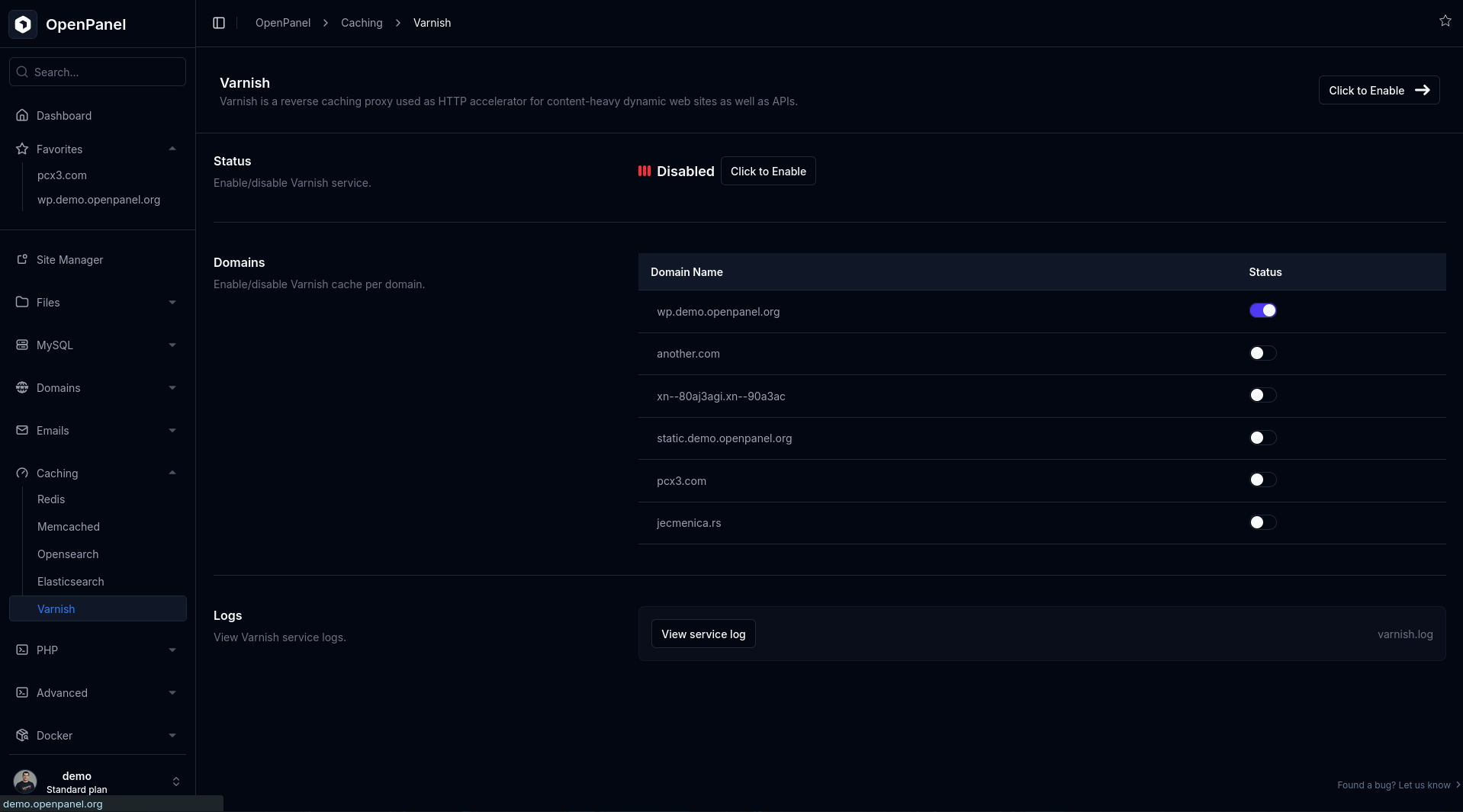
3. Disable Varnish Cache
Sometimes a 502 error is cached by Varnish, even if the backend issue is resolved. If you are using Varnish Cache:
Steps:
- Go to Caching > Varnish and disable it for the affected domain.
- Reload the website in your browser.
You can also bypass cache by adding parameters to the URL:
- Example:
example.net?testorexample.net?cachebypass
If disabling Varnish resolves the issue, stop and start it to clear all cached entries.
4. Verify VirtualHosts
A misconfigured VirtualHost may cause Nginx to proxy requests to a backend that no longer exists. if you have access to the edit_vhost feature:
Steps:
- Go to Domains > [Select Domain] > Edit VHosts.
- Check the proxy target (e.g., PHP service name or container).
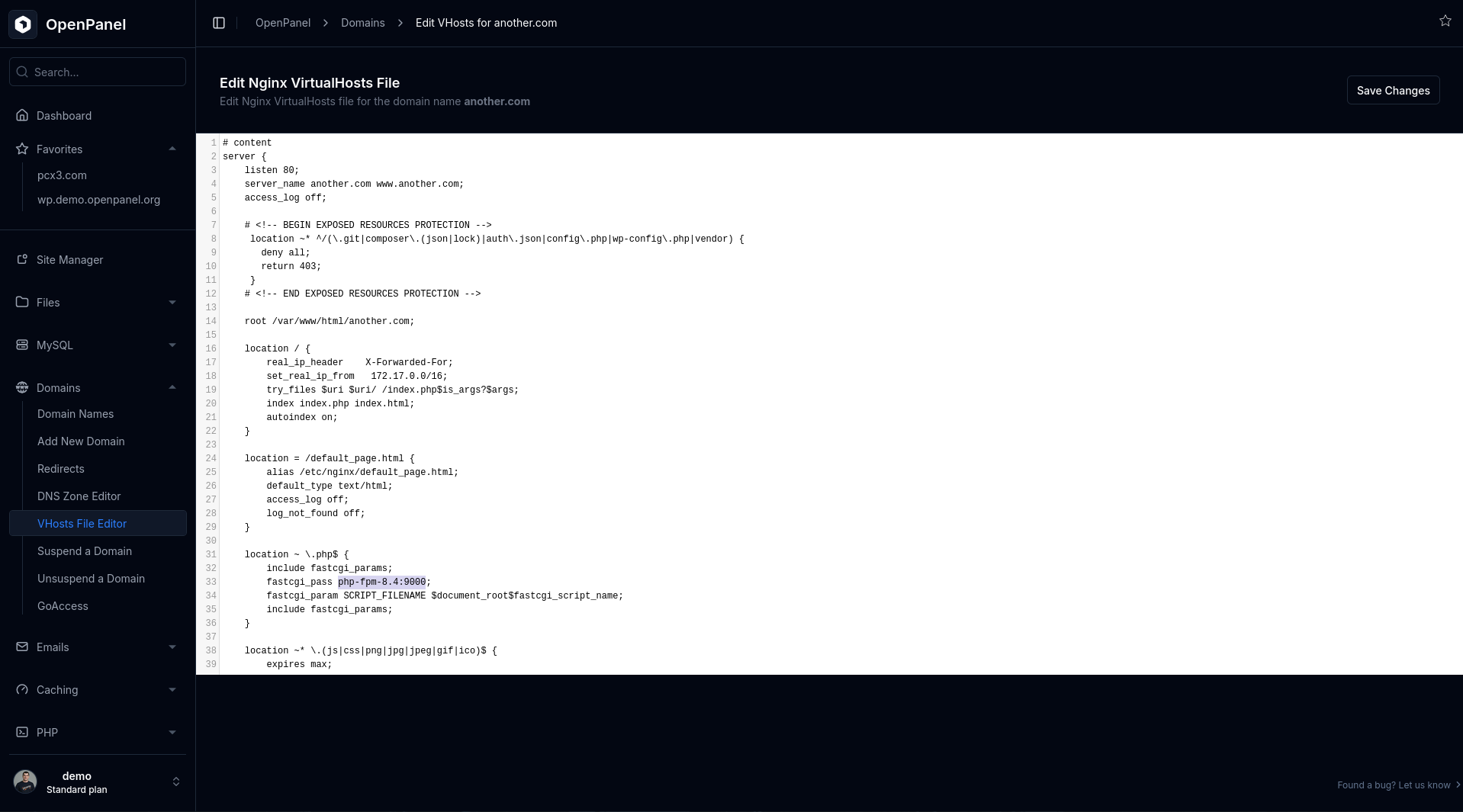
- Ensure the service name is spelled correctly and still exists.
With these steps, you should be able to identify and fix the most common causes of 502 Bad Gateway errors.