404 Error Troubleshooting Guide
This guide explains the most common causes of 404 Not Found errors on a website and how to resolve them.
1. File Does Not Exist
The simplest and most common cause: the file isn’t there. If you are requesting a static file, make sure it actually exists in the specified path or document root.
Example:
If you request example.com/index.html, confirm that index.html exists in the document root of the domain example.com.
How to check:
- Go to Domains > [Your Domain] > click on Document Root.
- Open the File Manager and verify that the file is present in the correct location.
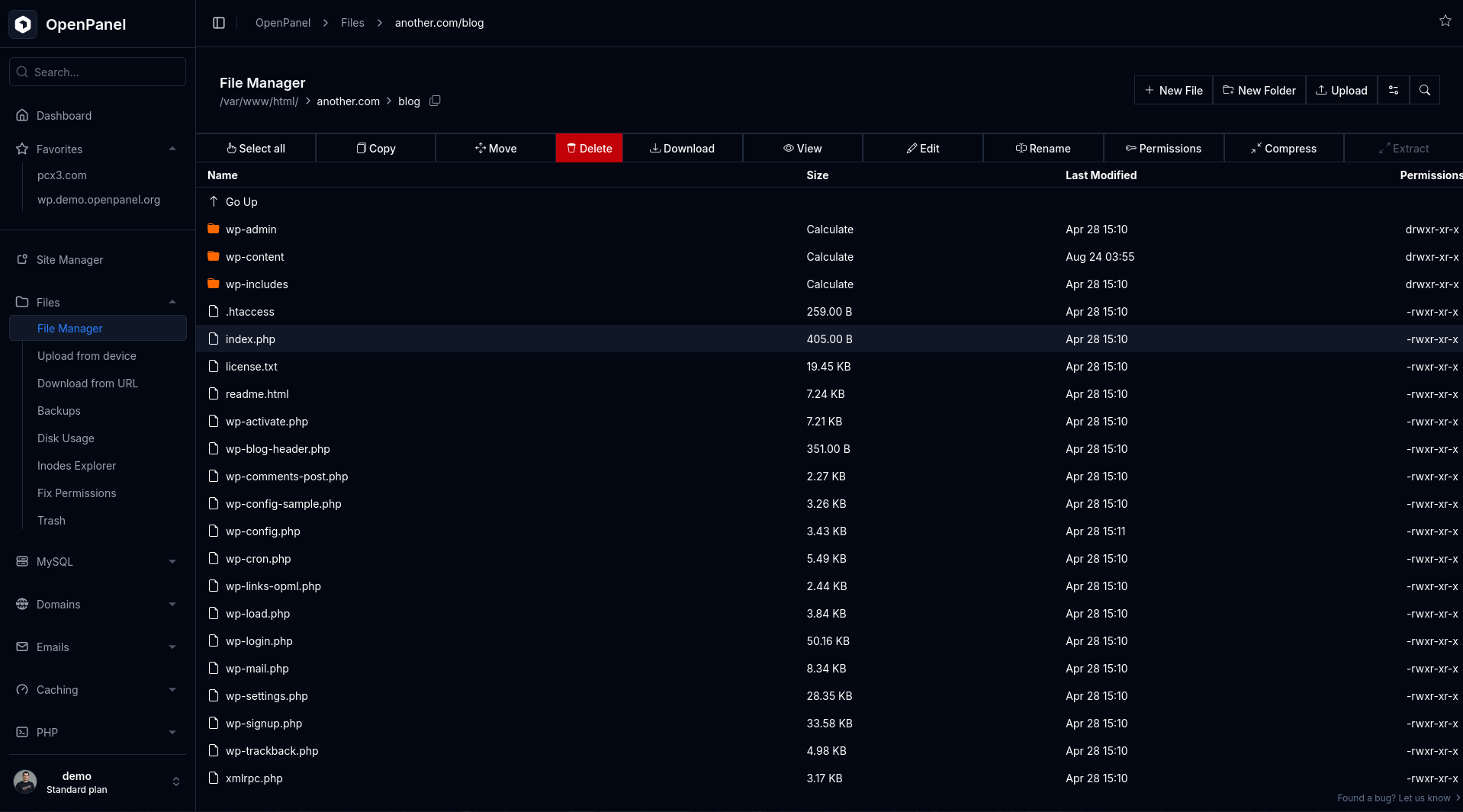
2. Rewrite Rules
If the request is for a dynamic route (e.g., WordPress pretty permalinks such as example.com/about), the issue may be caused by misconfigured rewrite rules in your .htaccess file or VirtualHosts configuration.
For Apache or LiteSpeed:
- Open the File Manager and check for a
.htaccessfile in the domain’s document root.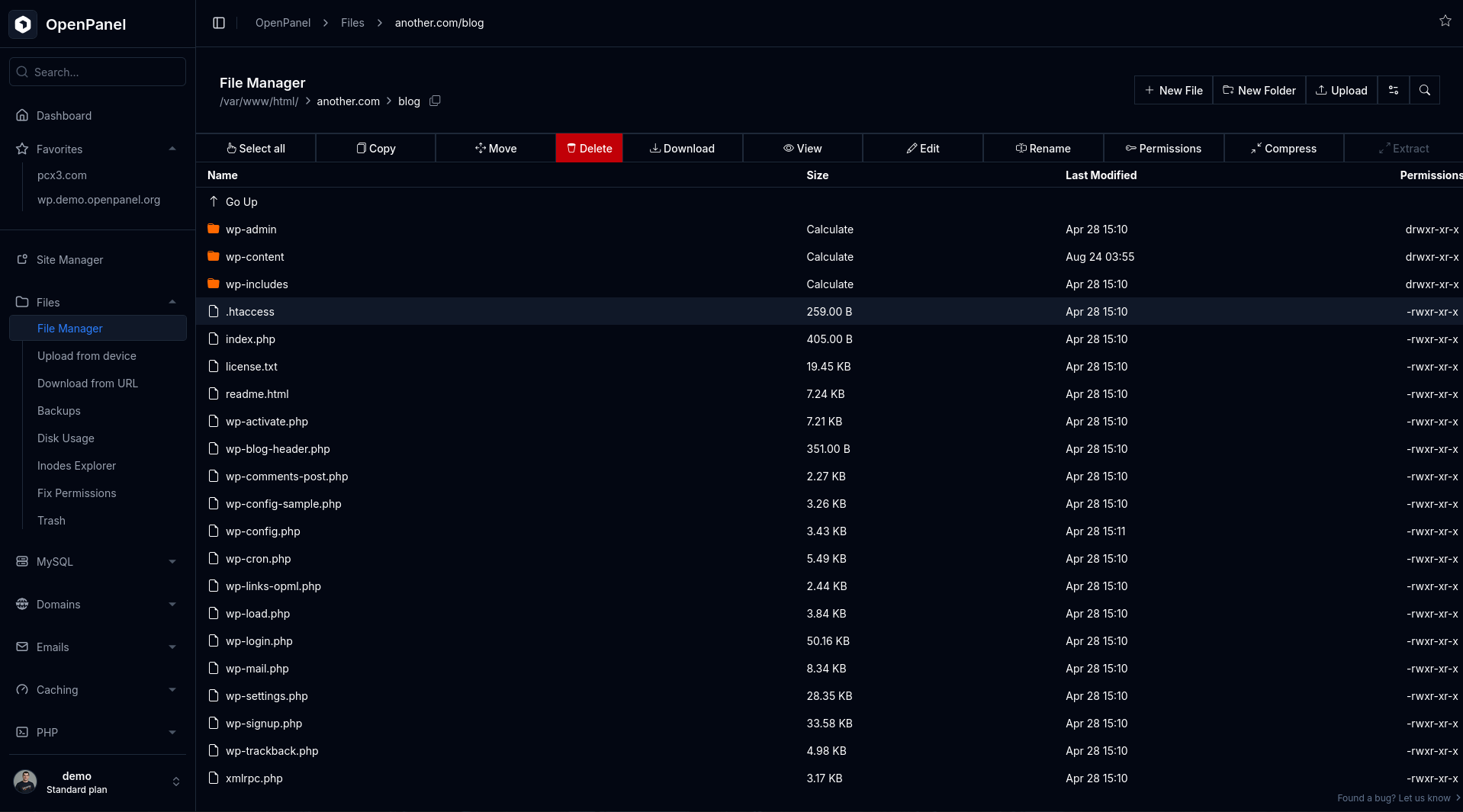
- If it exists, review its contents.
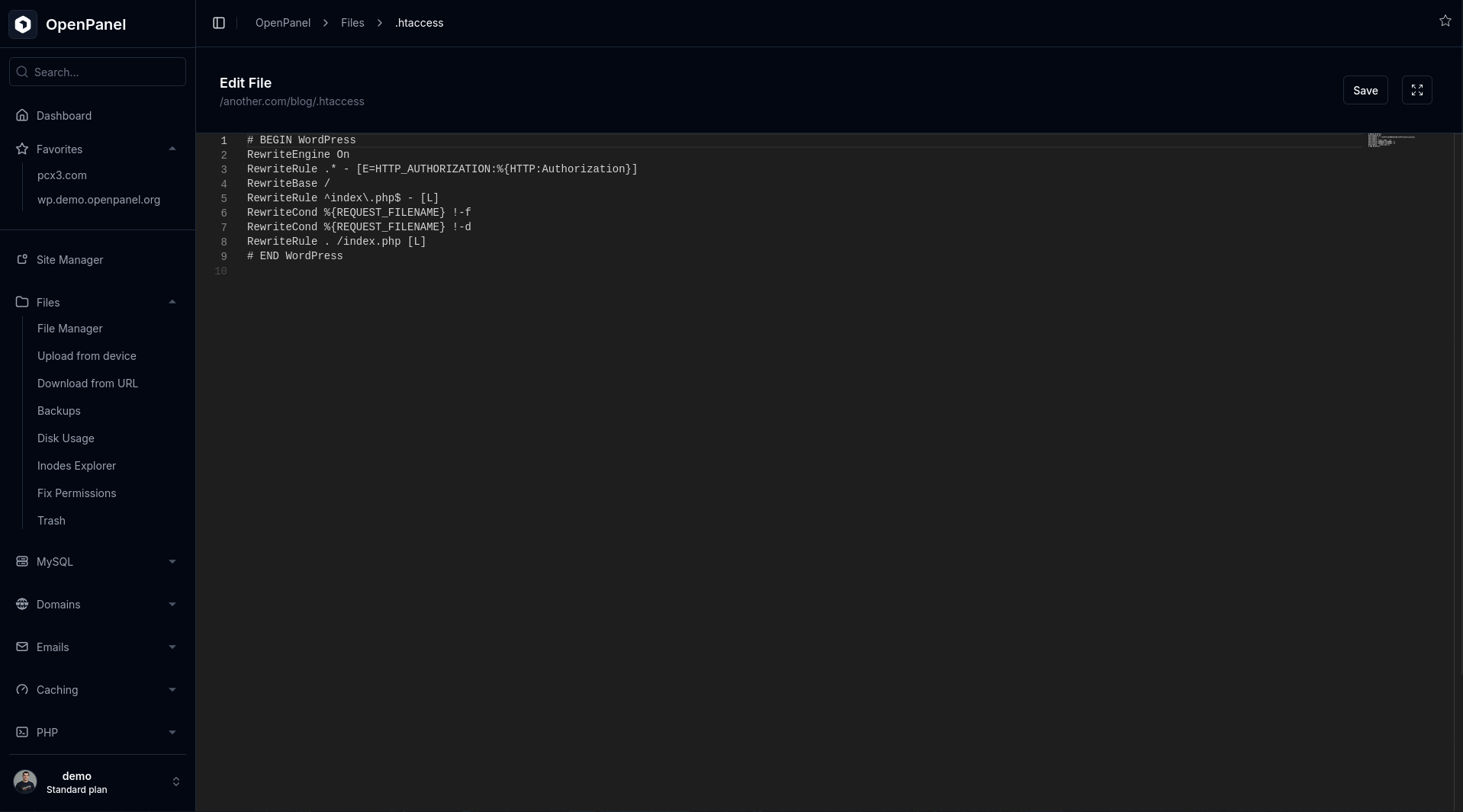
- For WordPress, you can simply go to WP Admin > Settings > Permalinks and click Save (even without changes). This refreshes the rewrite rules in
.htaccess. - Restart the webserver afterward to apply the changes from .htaccess file.
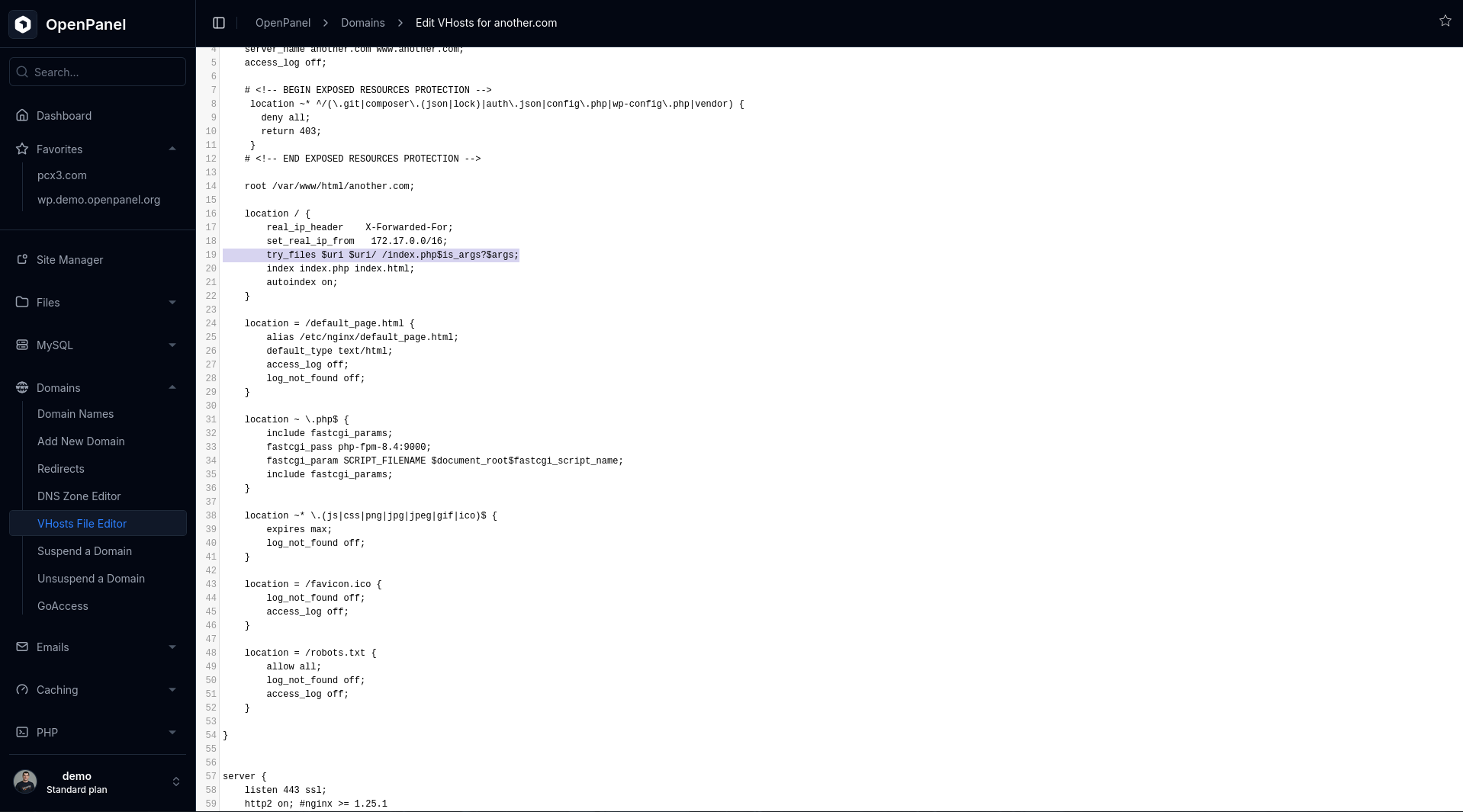
For Nginx or OpenResty:
.htaccessfiles are not used. Rewrite rules are set directly in the VirtualHosts configuration.- Go to Domains > [Your Domain] > Edit VHosts.
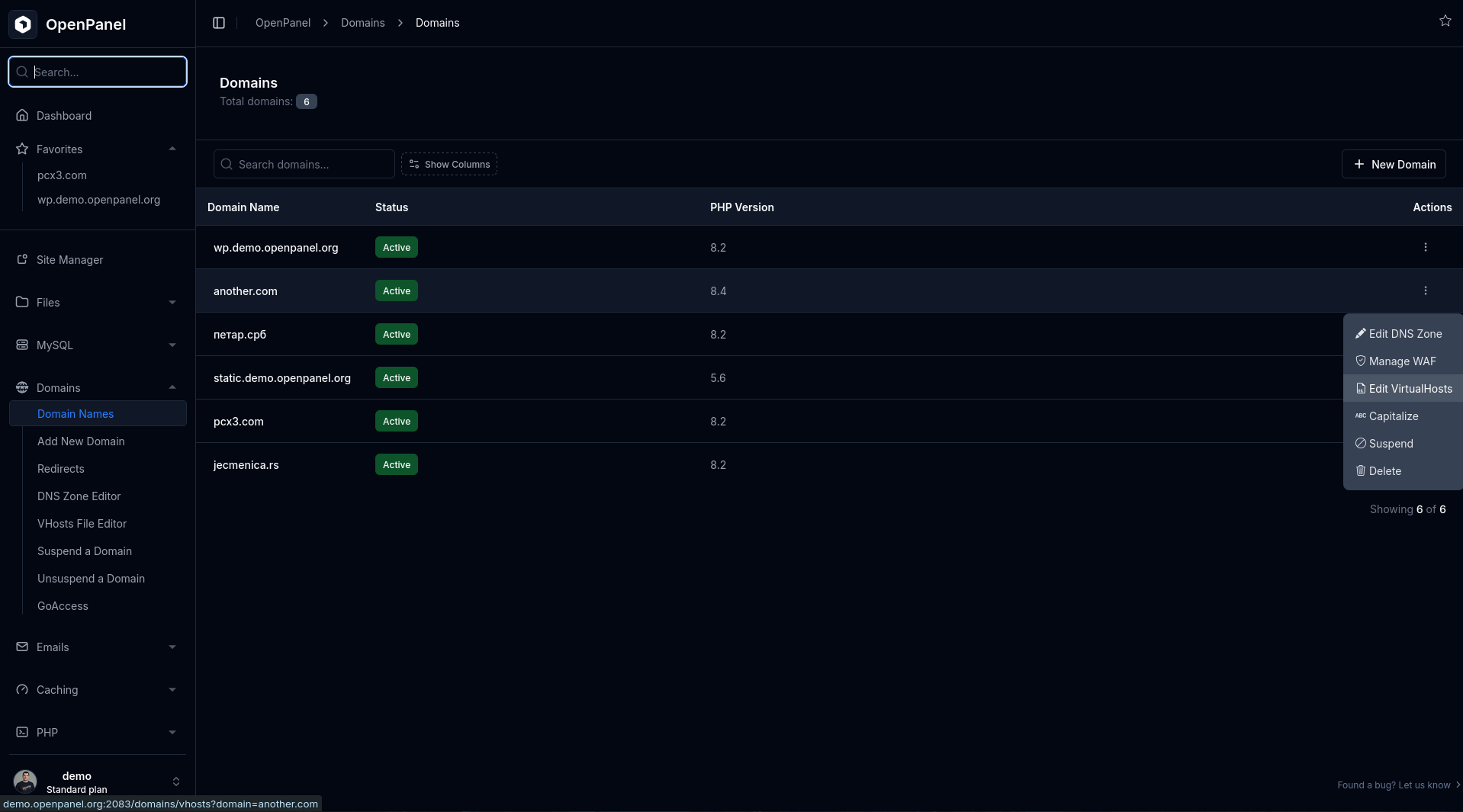
- Review and correct the rewrite rules, then save the file. This automatically reloads the webserver to apply changes.
After adjustments, test your website again.
3. Docker Mount Issues
In rare cases, Docker’s file mounting system (which uses inodes) can cause discrepancies. If a user or program has moved or renamed a home directory, the PHP service container may no longer see the same files as the File Manager.
This means the file might appear in File Manager but not be accessible to PHP.
How to check:
If you have Docker access:
Go to Docker > Terminal.
Select the PHP service.
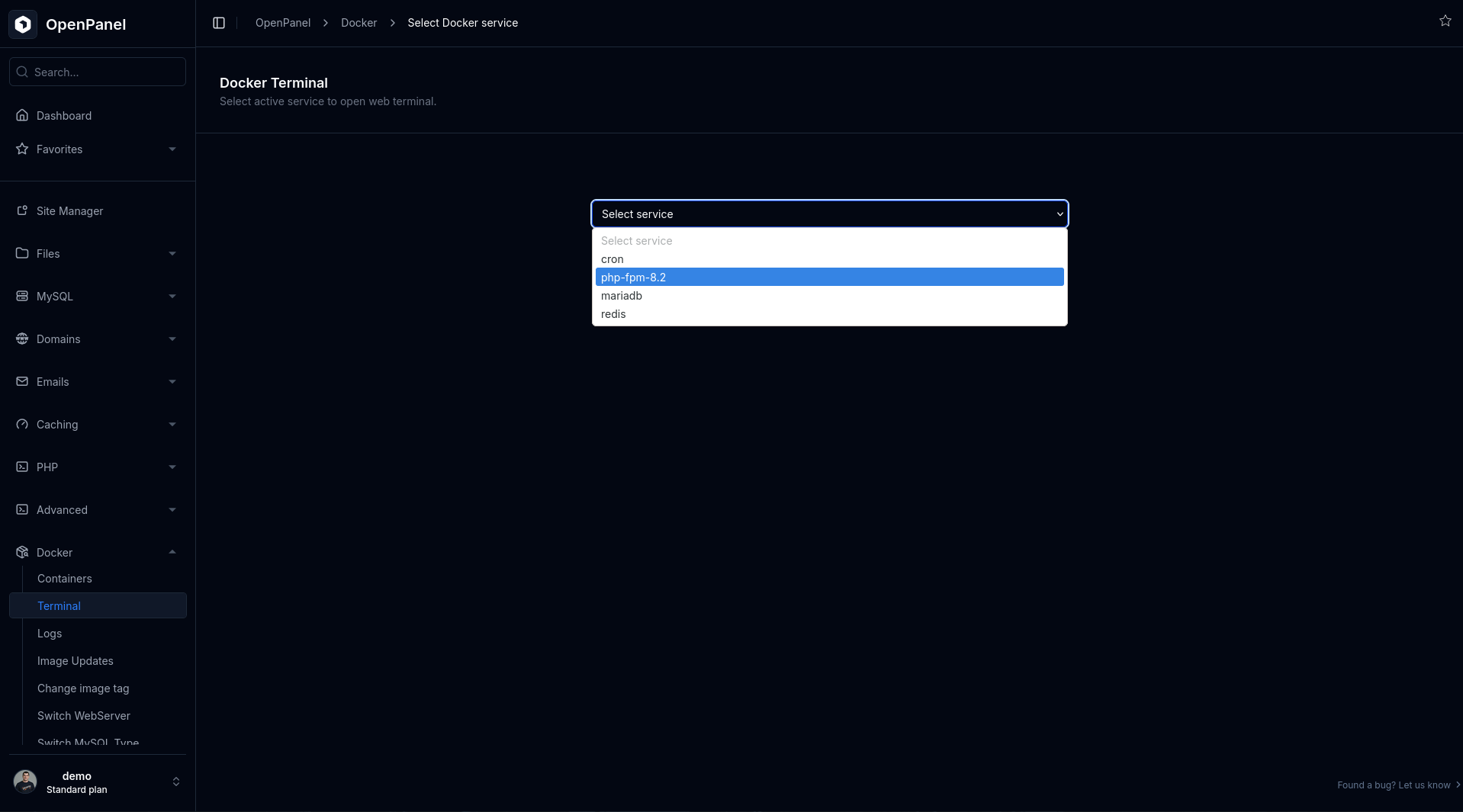
Run:
ls filename_here.phpIf the file does not appear, restart the PHP service to remount.
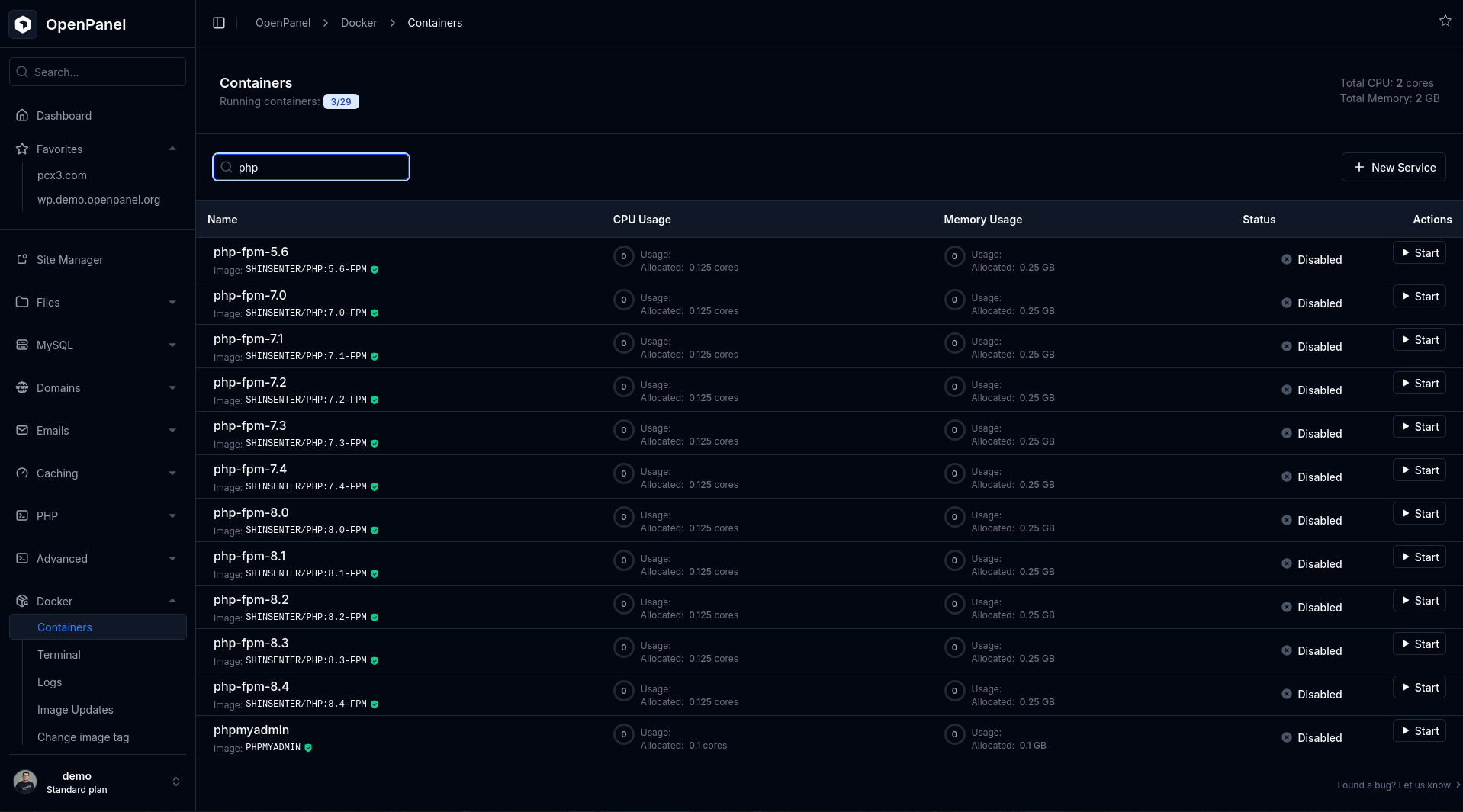
To restart the PHP container:
- Go to Docker > Containers.
- Disable the PHP service, wait for the page to reload, then enable it again.
If you do not have Docker access:
- Contact your hosting provider and request a PHP service restart.
Once done, verify the file again using the terminal.